The Bench Team Chronicle
Insightful news and updates from the world of sports and teamwork.
Sugar Dilemma: Navigating Life with Diabetes
Discover effective tips and real-life stories to conquer diabetes challenges. Empower your journey to a healthier, sweeter life today!
Understanding Carbohydrates: How They Affect Blood Sugar Levels
Carbohydrates are one of the three macronutrients that provide energy for our bodies, and they play a crucial role in regulating blood sugar levels. When consumed, carbohydrates are broken down into glucose, which is then released into the bloodstream. This process can lead to fluctuations in blood sugar levels depending on the type of carbohydrate consumed. Simple carbohydrates, found in sugary foods and drinks, can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar, while complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains and legumes, are digested more slowly, resulting in a gradual increase in blood sugar levels. Understanding the difference between these types of carbohydrates is key to managing your blood sugar effectively.
For those looking to maintain stable blood sugar levels, it's important to consider the glycemic index (GI) of foods. The GI measures how quickly a carbohydrate-containing food raises blood sugar levels. Foods with a high GI can lead to quick spikes and crashes in energy, whereas low-GI foods tend to provide a more stable release of glucose into the bloodstream. To promote healthy blood sugar levels, include more low-GI options in your diet, such as whole grains, vegetables, and fruits. Additionally, pairing carbohydrates with protein or healthy fats can further stabilize blood sugar levels and improve overall health.
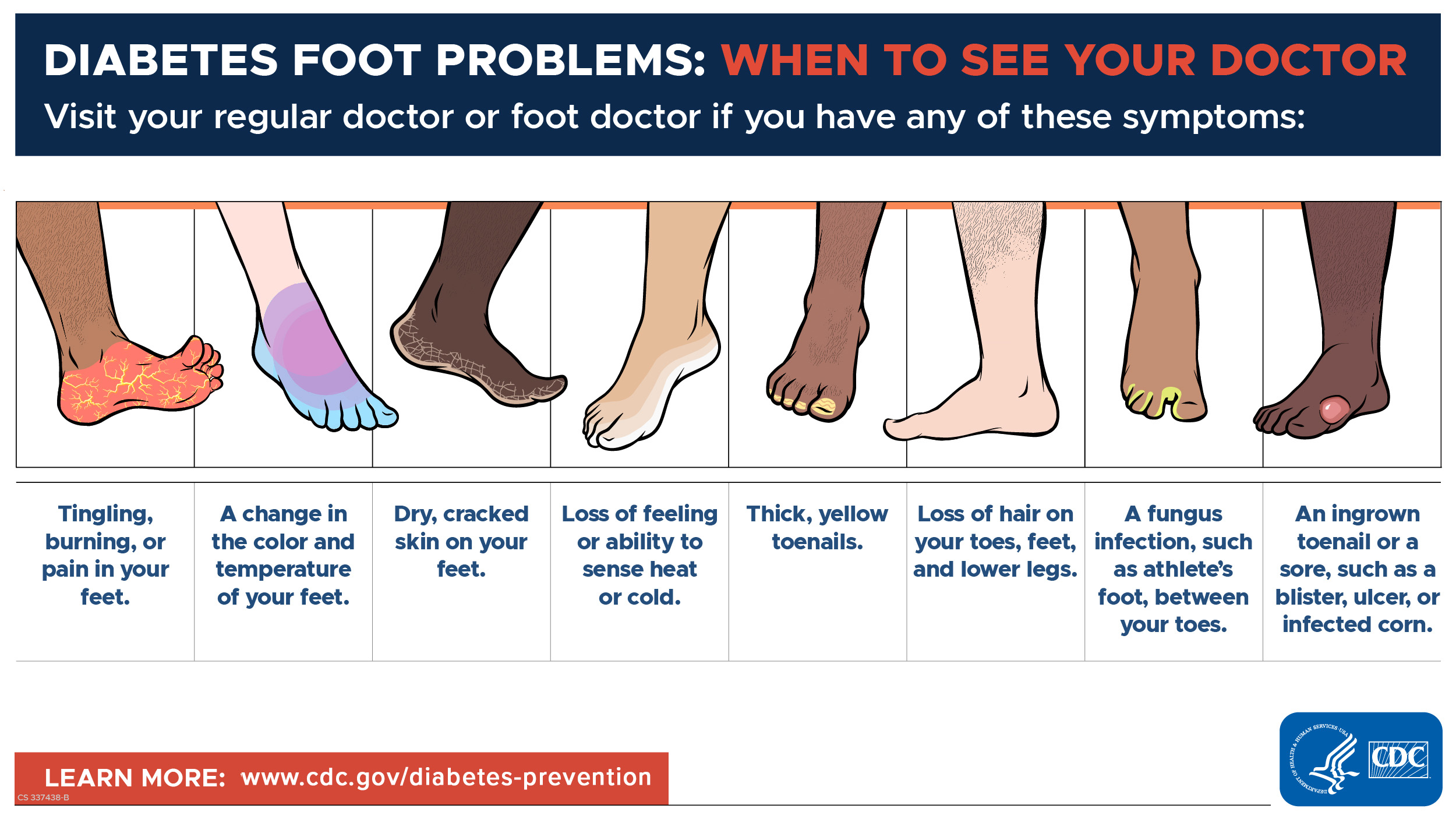
10 Smart Snacking Tips for Diabetes Management
Managing diabetes doesn't mean you have to sacrifice snacking. In fact, smart snacking can be an essential part of maintaining stable blood sugar levels. Here are 10 smart snacking tips for diabetes management:
- Choose Whole Foods: Opt for snacks like fruits, vegetables, nuts, and whole grains.
- Mind the Portions: Keep your portions in check to avoid spikes in blood sugar.
- Pair Protein with Carbs: Combine carbohydrates with protein to slow down sugar absorption.
Additionally, it's important to stay hydrated and make conscious food choices. Smart snacking can be a game-changer for those managing diabetes. Consider these tips:
- Plan Your Snacks: Have healthy snacks on hand to avoid impulsive eating.
- Incorporate Healthy Fats: Include snacks like avocados or olive oil to promote satiety.
- Avoid Sugary Snacks: Steer clear of items high in added sugars, as they can cause drastic fluctuations in blood sugar levels.
The Truth About Sugar Substitutes: Which Ones Are Safe?
As more people become health-conscious, the demand for sugar substitutes has surged. However, not all sugar alternatives are created equal. Some, like stevia and erythritol, have gained popularity due to their natural origins and lower calorie content, making them safer options for those looking to reduce sugar intake. On the other hand, artificial sweeteners such as aspartame and saccharin have been the subjects of extensive debate regarding their safety. While regulatory agencies have deemed many of these artificial substitutes safe for consumption, there are still concerns about their long-term effects on health.
When evaluating the safety of various sugar substitutes, consider the following factors:
- Natural vs. Artificial: Natural sweeteners often have fewer side effects than their artificial counterparts.
- Caloric Content: Some substitutes can offer sweetness without the added calories, making them appealing for weight management.
- Sugar Alcohols: Ingredients like xylitol and maltitol can cause digestive issues for some individuals, so moderation is key.